Simple Mesh
Here, we consider generating rectangular domain nodes (2D) and cuboidal domain nodes (3D) by controlling the starting range and step size in each direction.
2D
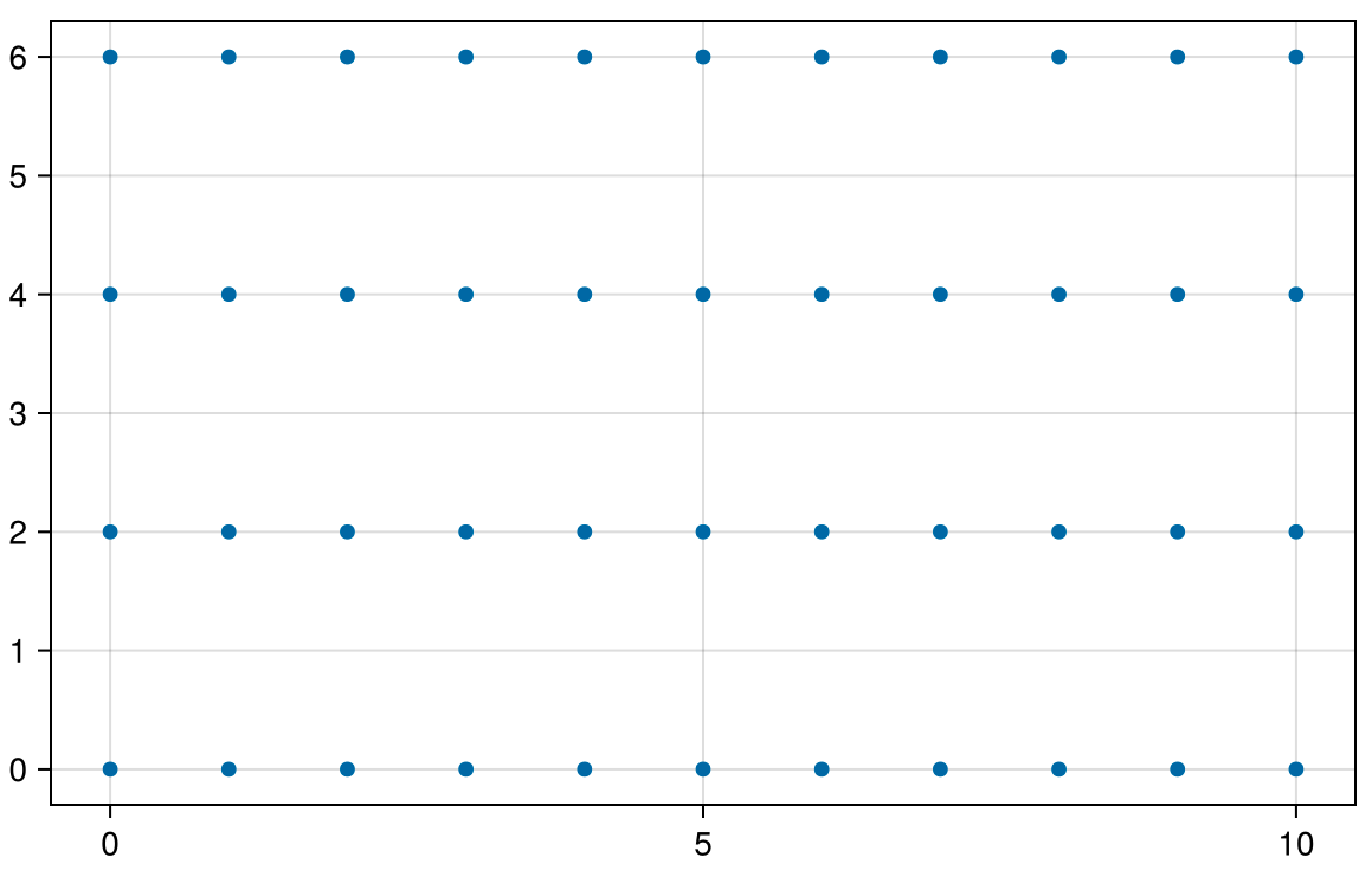
Consider a rectangular area where the range in the x-direction is from 0 to 10 and in the y-direction from 0 to 6. The step size in the x-direction is 1, and in the y-direction, it is 2. Therefore, we can do:
MaterialPointGenerator.meshbuilder Method
meshbuilder(x::T, y::T; ϵ::String="FP64") where T <: AbstractRangeDescription:
Generate structured mesh in 2D space.
sourcejulia> pts = meshbuilder(0.0 : 1.0 : 10.0, 0.0: 2.0 : 6.0)
44×2 Matrix{Float64}:
0.0 0.0
0.0 2.0
0.0 4.0
0.0 6.0
1.0 0.0
1.0 2.0
⋮
9.0 6.0
10.0 0.0
10.0 2.0
10.0 4.0
10.0 6.0This way, we can obtain the results shown in the figure. The variable pts is an array where the first column contains the x-coordinates of all the nodes, and the second column contains the corresponding y-coordinates.
3D
Similarly, we can use this function to generate a set of points in three-dimensional space.
MaterialPointGenerator.meshbuilder Method
meshbuilder(x::T, y::T, z::T; ϵ::String="FP64") where T <: AbstractRangeDescription:
Generate structured mesh in 3D space.
sourcejulia> pts = meshbuilder(0.0 : 1.0 : 10.0, 0.0: 2.0 : 6.0, 0.0 : 2.0 : 4.0)
132×3 Matrix{Float64}:
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 2.0 0.0
0.0 4.0 0.0
0.0 6.0 0.0
1.0 0.0 0.0
1.0 2.0 0.0
⋮
9.0 6.0 4.0
10.0 0.0 4.0
10.0 2.0 4.0
10.0 4.0 4.0
10.0 6.0 4.0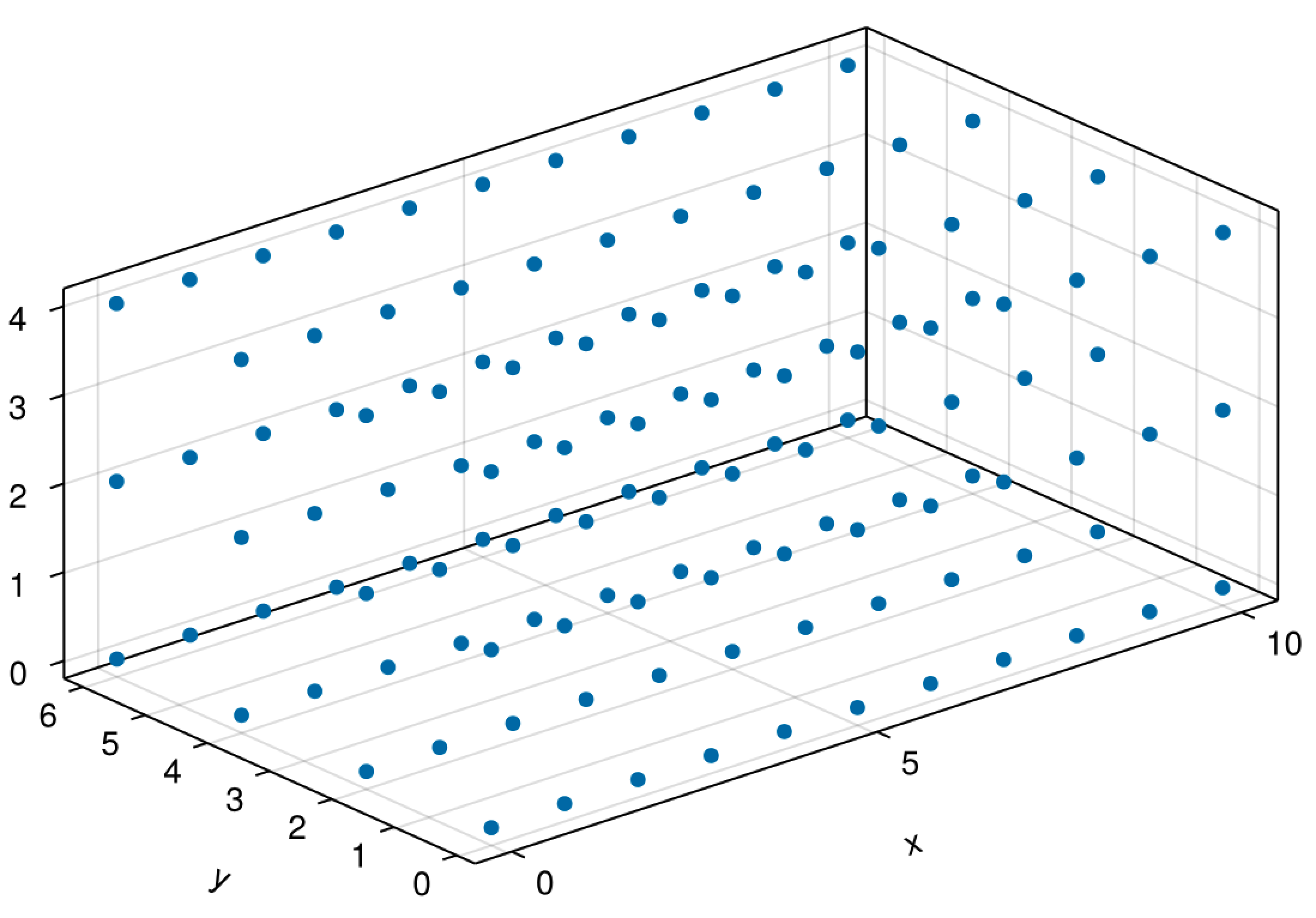
Export
For two-dimensional points and three-dimensional points, you can use the functions savexy and savexyz to save them as .xy and .xyz files, respectively. You can also use readxy and readxyz to read these files.
MaterialPointGenerator.savexy Method
savexy(file_dir::P, pts::T) where {P <: String, T <: AbstractMatrix}Description:
Save the 2D points pts to the .xy file (file_dir).
MaterialPointGenerator.savexyz Method
savexyz(file_dir::P, pts::T) where {P <: String, T <: AbstractMatrix}Description:
Save the 3D points pts to the .xyz file (file_dir).
MaterialPointGenerator.readxy Method
readxy(file_dir::P) where P <: StringDescription:
Read the 2D .xy file from file_dir.
MaterialPointGenerator.readxyz Method
readxyz(file_dir::P) where P <: StringDescription:
Read the 3D .xyz file from file_dir.
output_file = joinpath(@__DIR__, "test.xyz")
savexyz(output_file, pts)
data = readxyz(output_file)