One-phase single-point MPM
Note
We use a classic example: 2D & 3D granular collapse[1], to demonstrate how to establish computational models and solve them.
To successfully run the code, we will install the dependencies at the beginning of the code provided below. If you are already familiar with the Julia Pkg ENV and have installed the necessary packages, you can ignore this part.
We default to using Nvidia's GPU or x86/ARM CPUs. If you want to use other acceleration backends, please make modifications in the appropriate places in the code.
We use Unicode to enhance readability (when comparing formulas), but sometimes it may be confused with regular letters, such as
and v. If you are using VSCode, you can enable the following in the settings:
"editor.unicodeHighlight.ambiguousCharacters": true,- You can copy and save it in the
your_file.jland run the file directly using Julia inREPL:
julia> include("path/to/your_file.jl")Or run this file in the terminal:
bash> julia path/to/your_file.jlHere is the complete 2D code
using Pkg
Pkg.add(["MaterialPointSolver", "MaterialPointGenerator", "CairoMakie", "CUDA"])
using MaterialPointSolver
using MaterialPointGenerator
using CairoMakie
using CUDA
MaterialPointSolver.warmup(Val(:CUDA))
init_grid_space_x = 0.0025
init_grid_space_y = 0.0025
init_grid_range_x = [-0.025, 0.82]
init_grid_range_y = [-0.025, 0.12]
init_mp_in_space = 2
init_T = 1
init_ρs = 2650
init_ν = 0.3
init_Ks = 7e5
init_Es = init_Ks * (3 * (1 - 2 * init_ν))
init_Gs = init_Es / (2 * (1 + init_ν))
init_ΔT = 0.5 * init_grid_space_x / sqrt(init_Es / init_ρs)
init_step = floor(init_T / init_ΔT / 200)
init_ϕ = deg2rad(19.8)
init_NIC = 9
init_basis = :uGIMP
init_ϵ = "FP64"
# args setup
args = UserArgs2D(
Ttol = init_T,
Te = 0,
ΔT = init_ΔT,
time_step = :fixed,
FLIP = 1,
PIC = 0,
constitutive = :druckerprager,
basis = init_basis,
hdf5 = false,
hdf5_step = init_step,
MVL = false,
device = :CPU,
coupling = :OS,
scheme = :MUSL,
progressbar = true,
gravity = -9.8,
ζs = 0,
project_name = "2d_collapse",
project_path = @__DIR__,
ϵ = init_ϵ
)
# grid setup
grid = UserGrid2D(
ϵ = init_ϵ,
phase = 1,
x1 = init_grid_range_x[1],
x2 = init_grid_range_x[2],
y1 = init_grid_range_y[1],
y2 = init_grid_range_y[2],
dx = init_grid_space_x,
dy = init_grid_space_y,
NIC = init_NIC
)
# material point setup
dx = grid.dx / init_mp_in_space
dy = grid.dy / init_mp_in_space
ξ0 = meshbuilder(0 + dx / 2 : dx : 0.2 - dx / 2,
0 + dy / 2 : dy : 0.1 - dy / 2)
mp = UserParticle2D(
ϵ = init_ϵ,
phase = 1,
NIC = init_NIC,
dx = dx,
dy = dy,
ξ = ξ0,
ρs = ones(size(ξ0, 1)) .* init_ρs
)
# property setup
nid = ones(mp.np)
attr = UserProperty(
ϵ = init_ϵ,
nid = nid,
ν = [init_ν],
Es = [init_Es],
Gs = [init_Gs],
Ks = [init_Ks],
σt = [0],
ϕ = [init_ϕ],
ϕr = [0],
ψ = [0],
c = [0],
cr = [0],
Hp = [0]
)
# boundary setup
vx_idx = zeros(grid.ni)
vy_idx = zeros(grid.ni)
tmp_idx = findall(i -> grid.ξ[i, 1] ≤ 0.0 || grid.ξ[i, 1] ≥ 0.8 ||
grid.ξ[i, 2] ≤ 0, 1:grid.ni)
tmp_idy = findall(i -> grid.ξ[i, 2] ≤ 0, 1:grid.ni)
vx_idx[tmp_idx] .= 1
vy_idx[tmp_idy] .= 1
bc = UserVBoundary2D(
ϵ = init_ϵ,
vx_s_idx = vx_idx,
vx_s_val = zeros(grid.ni),
vy_s_idx = vy_idx,
vy_s_val = zeros(grid.ni)
)
# solver setup
materialpointsolver!(args, grid, mp, attr, bc)
# post-processing
let
figregular = MaterialPointSolver.tnr
figbold = MaterialPointSolver.tnrb
fig = Figure(size=(440, 142), fonts=(; regular=figregular, bold=figbold), fontsize=12,
padding=0)
ax = Axis(fig[1, 1], aspect=DataAspect(), xlabel=L"x\ (m)", ylabel=L"y\ (m)",
xticks=(0:0.1:0.5), yticks=(0:0.05:0.1))
p1 = scatter!(ax, mp.ξ, color=log10.(mp.ϵq.+1), markersize=2, colormap=:turbo,
colorrange=(0, 1.5))
Colorbar(fig[1, 2], p1, spinewidth=0, label=L"log_{10}(\epsilon_{II}+1)", size=6)
limits!(ax, -0.02, 0.52, -0.02, 0.12)
display(fig)
endHere is the complete 3D code
using Pkg
Pkg.add(["MaterialPointSolver", "MaterialPointGenerator", "CairoMakie", "CUDA"])
using MaterialPointSolver
using MaterialPointGenerator
using CairoMakie
using CUDA
MaterialPointSolver.warmup(Val(:CUDA))
init_grid_space_x = 0.0025
init_grid_space_y = 0.0025
init_grid_space_z = 0.0025
init_grid_range_x = [-0.02, 0.07]
init_grid_range_y = [-0.02, 0.75]
init_grid_range_z = [-0.02, 0.12]
init_mp_in_space = 2
init_T = 1
init_ρs = 2650
init_ν = 0.3
init_Ks = 7e5
init_Es = init_Ks * (3 * (1 - 2 * init_ν))
init_Gs = init_Es / (2 * (1 + init_ν))
init_ΔT = 0.5 * init_grid_space_x / sqrt(init_Es / init_ρs)
init_step = floor(init_T / init_ΔT / 50)
init_ϕ = deg2rad(19.8)
init_FP = "FP64"
init_basis = :uGIMP
init_NIC = 27
# args setup
args = UserArgs3D(
Ttol = init_T,
Te = 0,
ΔT = init_ΔT,
time_step = :fixed,
FLIP = 1,
PIC = 0,
constitutive = :druckerprager,
basis = init_basis,
hdf5 = false,
hdf5_step = init_step,
MVL = false,
device = :CUDA,
coupling = :OS,
scheme = :MUSL,
gravity = -9.8,
ζs = 0,
project_name = "3d_collapse",
project_path = @__DIR__,
ϵ = init_FP
)
# grid setup
grid = UserGrid3D(
ϵ = init_FP,
phase = 1,
x1 = init_grid_range_x[1],
x2 = init_grid_range_x[2],
y1 = init_grid_range_y[1],
y2 = init_grid_range_y[2],
z1 = init_grid_range_z[1],
z2 = init_grid_range_z[2],
dx = init_grid_space_x,
dy = init_grid_space_y,
dz = init_grid_space_z,
NIC = init_NIC
)
# material point setup
dx = grid.dx / init_mp_in_space
dy = grid.dy / init_mp_in_space
dz = grid.dz / init_mp_in_space
pts = meshbuilder(0 + dx / 2 : dx : 0.05 - dx / 2,
0 + dy / 2 : dy : 0.20 - dy / 2,
0 + dz / 2 : dz : 0.10 - dz / 2)
mpρs = ones(size(pts, 1)) * init_ρs
mp = UserParticle3D(
ϵ = init_FP,
phase = 1,
NIC = init_NIC,
dx = dx,
dy = dy,
dz = dz,
ξ = pts,
ρs = mpρs
)
# property setup
nid = ones(mp.np)
attr = UserProperty(
ϵ = init_FP,
nid = nid,
ν = [init_ν],
Es = [init_Es],
Gs = [init_Gs],
Ks = [init_Ks],
σt = [0],
ϕ = [init_ϕ],
ϕr = [0],
ψ = [0],
c = [0],
cr = [0],
Hp = [0]
)
# boundary setup
vx_idx = zeros(grid.ni)
vy_idx = zeros(grid.ni)
vz_idx = zeros(grid.ni)
tmp_idx = findall(i -> grid.ξ[i, 1] ≤ 0 || grid.ξ[i, 1] ≥ 0.05 ||
grid.ξ[i, 3] ≤ 0 || grid.ξ[i, 2] ≤ 0, 1:grid.ni)
tmp_idy = findall(i -> grid.ξ[i, 2] ≤ 0 || grid.ξ[i, 3] ≤ 0, 1:grid.ni)
tmp_idz = findall(i -> grid.ξ[i, 3] ≤ 0, 1:grid.ni)
vx_idx[tmp_idx] .= 1
vy_idx[tmp_idy] .= 1
vz_idx[tmp_idz] .= 1
bc = UserVBoundary3D(
ϵ = init_FP,
vx_s_idx = vx_idx,
vx_s_val = zeros(grid.ni),
vy_s_idx = vy_idx,
vy_s_val = zeros(grid.ni),
vz_s_idx = vz_idx,
vz_s_val = zeros(grid.ni)
)
# solver setup
materialpointsolver!(args, grid, mp, attr, bc)
# post-processing
let
figfont = MaterialPointSolver.tnr
fig = Figure(size=(1200, 700), fonts=(; regular=figfont, bold=figfont), fontsize=30)
ax = Axis3(fig[1, 1], xlabel=L"x\ (m)", ylabel=L"y\ (m)", zlabel=L"z\ (m)",
aspect=:data, azimuth=0.2*π, elevation=0.1*π, xlabeloffset=60, zlabeloffset=80,
protrusions=100, xticks=(0:0.04:0.04), height=450, width=950)
pl1 = scatter!(ax, mp.ξ, color=log10.(mp.ϵq.+1), colormap=:jet, markersize=3,
colorrange=(0, 1))
Colorbar(fig[1, 1], limits=(0, 1), colormap=:jet, size=16, ticks=0:0.5:1, spinewidth=0,
label=L"log_{10}(\epsilon_{II}+1)", vertical=false, tellwidth=false, width=200,
halign=:right, valign=:top, flipaxis=false)
display(fig)
end2D model description
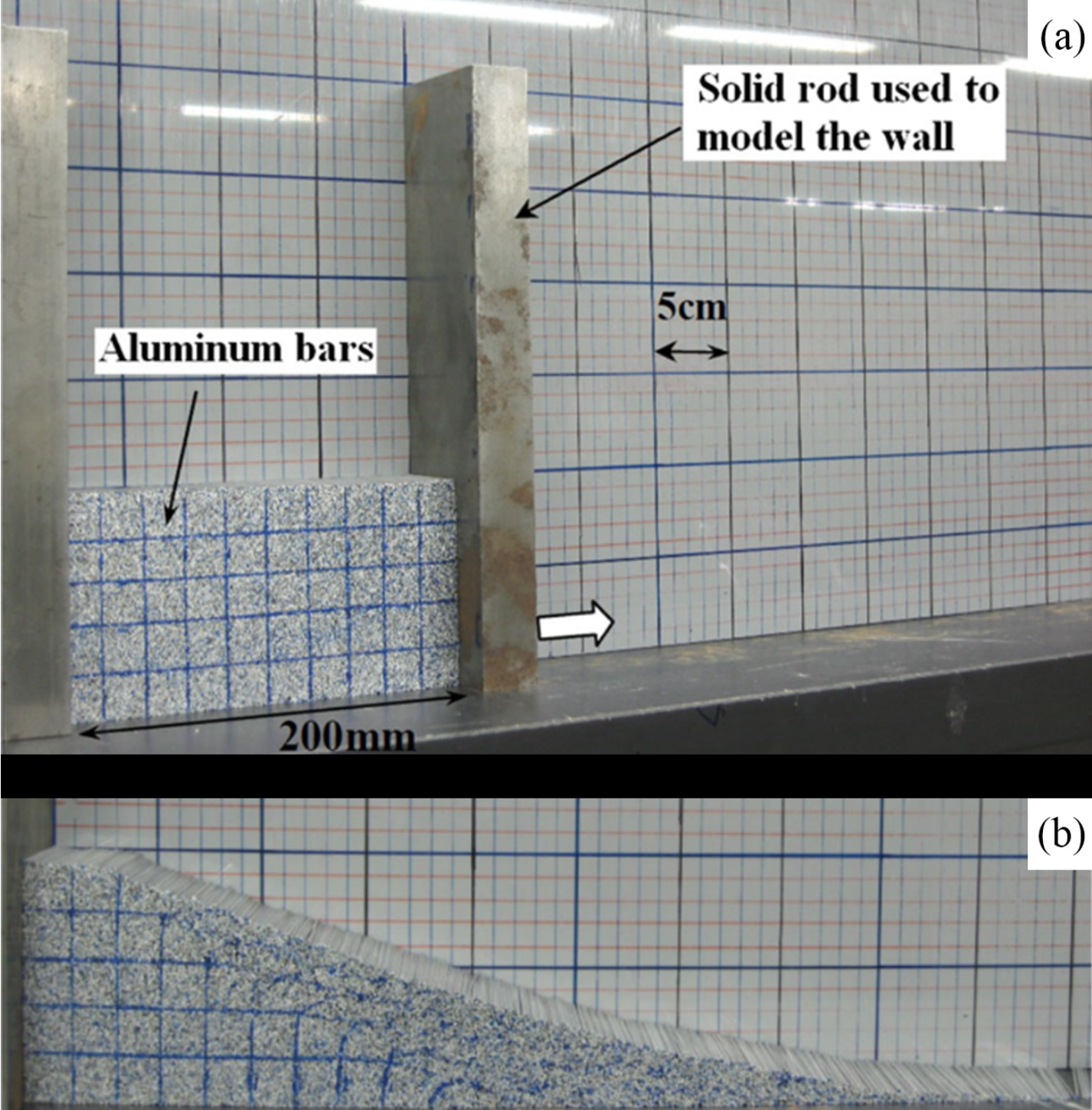
In this example, aluminum bars are used to model the non-cohesive soil collapse. We use uGIMP to simulate the failure process of soil collapse. The geometry of the numerical model is depicted in the figure, with a length
| Parameter | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| density | |||
| - | Poisson's ratio | ||
| bulk modulus | |||
| second | simulation time | ||
| degree | friction angle | ||
| - | FLIP-PIC mixing factor |
2D code explaination
Step1: We import the required packages and perform warming up (optional):
using MaterialPointSolver # MPM solver
using MaterialPointGenerator # Particle generator
using CairoMakie # post-processing
using CUDA # backend package
MaterialPointSolver.warmup(Val(:CUDA)) # warm-upStep2: Some values used in the simulation:
init_grid_space_x = 0.0025 # background grid space in x direction
init_grid_space_y = 0.0025 # background grid space in y direction
init_grid_range_x = [-0.025, 0.82] # background grid x range
init_grid_range_y = [-0.025, 0.12] # background grid y range
init_mp_in_space = 2 # there are 2 particles in x direction per cell, so 4 in total per cell
init_T = 1 # simulation time, here is 1 second
init_ρs = 2650 # particle density
init_ν = 0.3 # Poisson's ratio
init_Ks = 7e5 # bulk modulus
init_Es = init_Ks * (3 * (1 - 2 * init_ν)) # elastic modulus
init_Gs = init_Es / (2 * (1 + init_ν)) # shear modulus
init_ΔT = 0.5 * init_grid_space_x / sqrt(init_Es / init_ρs) # time step in second
init_step = floor(init_T / init_ΔT / 200) # save data into hdf5 per 200 time steps
init_ϕ = deg2rad(19.8) # friction angle
init_NIC = 9 # 9 is used for uGIMP in 2D
init_basis = :uGIMP # basis function
init_ϵ = "FP64" # computing precisionStep3: Initialize Args2D:
# args setup
args = UserArgs2D(
Ttol = init_T,
Te = 0,
ΔT = init_ΔT,
time_step = :fixed,
FLIP = 1,
PIC = 0,
constitutive = :druckerprager, # constitutive model
basis = init_basis,
hdf5 = false,
hdf5_step = init_step,
MVL = false,
device = :CPU, # use CPU for the simulation
coupling = :OS, # one-phase single-point mpm
scheme = :MUSL, # stress update scheme
progressbar = true,
gravity = -9.8,
ζs = 0, # damping force factor
project_name = "2d_collapse", # project name
project_path = @__DIR__, # project path
ϵ = init_ϵ
)3D model description
3D code explaination
Bui, H.H., Fukagawa, R., Sako, K., Ohno, S., 2008. Lagrangian meshfree particles method (SPH) for large deformation and failure flows of geomaterial using elastic–plastic soil constitutive model. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 32, 1537–1570. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.688 ↩︎